
Speaking of [eating less and eating more], everyone’s first reaction will probably be related to [losing weight].
The reasons given in most articles are nothing more than: eat less and eat more, so that the body will not be hungry for too long, thus accelerating metabolism and burning more calories; Or, eat less and eat more to reduce the burden on the intestines and stomach, so that the intestines and stomach can better digest and absorb nutrition.
However, we also know that the key to reducing fat lies in creating a calorie gap every day, not how much you eat individually at each meal. Under the condition of the same total intake, can using the method of eating less and eating more really effectively reduce fat?
Rumor 1: Eat less and eat more, increasing the amount of calories consumed by eating.
Eating consumes energy, which is true. It generally accounts for 15% of the calories of the food eaten. It is related to the type of food eaten and the difference is not small.
But!
Studies as early as around 1990 showed that under the condition of eating the same food content, the amount of calories consumed by the body to digest food has nothing to do with the number of meals.
Rumor 2: Eat less and eat more to increase basic metabolism
Other articles claim that by dividing the same amount of food into multiple portions, the body’s basic metabolism (BMR) can be improved.
A 2004 study: For young healthy women, the content and total amount of food provided per day remained constant for one and a half months. Group A ate 6 times a day, Group B ate 3 times a day, and sometimes randomly increased to 9 times. The results showed that after a period of time, the metabolic level of group A was slightly stronger than that of group B.
Sounds beautiful, doesn’t it?
If the more meals you eat, the more metabolism you can improve, then prepare the food for the day and eat all the food slowly in 24 hours at a constant and uniform speed. Theoretically, when the eating interval approaches zero indefinitely, the number of meals you eat will approach positive infinity indefinitely, and metabolism will approach positive infinity indefinitely…
But!
There have also been experiments that have proved that under the condition of equal total amount, eating twice, three times, four times, five times, six times, seven times a day… has no effect on basic metabolism at all.
Rumor 3: Eat less and eat more, reduce fat and increase muscle?
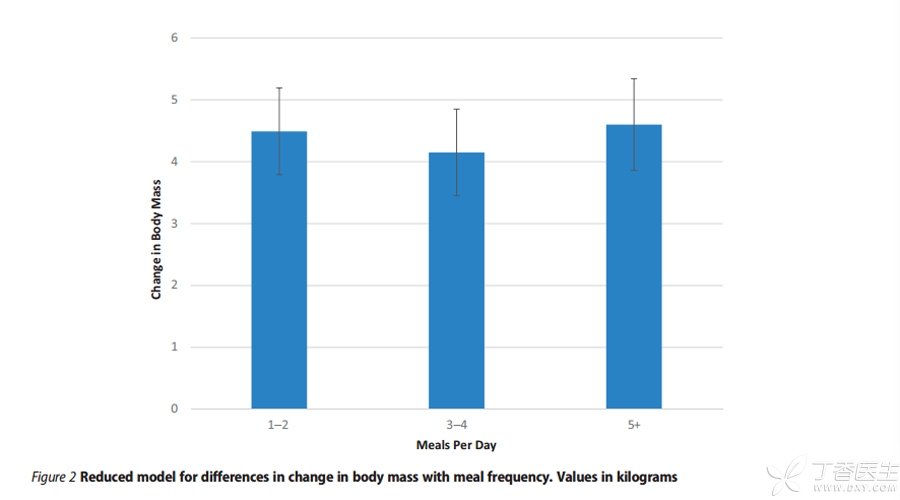
A meta-analysis was conducted in 2015 to study the effect of the number of meals eaten on changes in body weight, fat weight, lean body weight and body fat rate.
You may have seen the above histogram results in many articles, but if you only compare the height difference of the ordinate column, it is easy to draw the wrong conclusion: eating more than 5 meals a day is the most helpful to lose weight, followed by 1-2 meals a day, and 3 meals a day is the most unfavorable to lose weight; Eating less and eating more helps to reduce fat and maintain lean body weight.
But!
In fact, it is necessary to refer to statistical data, remove the study with the largest data deviation, and then draw the correct conclusion:
The difference between the effect of more than 5 meals and 3 meals per day on body weight is probably not more than 0.3 kg, that is, there is no significant difference.
The number of meals eaten has no significant effect on the reduction of fat, the maintenance of lean body weight and the reduction of body fat rate.
Seeing this, the conclusion should be very clear: the long-term effect of eating less and eating more is no different from the standard three meals a day or even one or two meals.
Eating less and eating more is really good!
Then why do many bodybuilders eat 6 or 7 meals a day?
One of the main reasons is that the energy intake of bodybuilders is much higher than that of normal people. Even during the fat reduction period, it is very common to have more than 3,000 kilocalories a day.
Too much food is divided into multiple meals, which can really reduce the burden on intestines and stomach.
Then why do many nutritionists recommend eating less and eating more everyday?
For maintaining a relatively stable blood sugar level, eating less and eating more does have a great effect.
Who is suitable to eat less and eat more?
Here are some tips:
- For hypoglycemic patients, eating less and eating more is helpful to stabilize blood sugar. For muscle-increasing people, when the total amount of food is relatively large, eating less and eating more is helpful to eat more and reduce the burden on intestines and stomach. People with small appetite will not exceed the total calories even if they eat more than one meal. People who are prone to gluttony, especially those who are manic when hungry, eat less and eat more can help control hunger on a daily basis.
On the contrary, if the appetite is relatively large, it is easy to go mad once the meal is not full, if the meal is five times a day, the most direct consequence is that the total energy intake exceeds the standard!
It is far more meaningful to pay attention to the total amount of food eaten every day than to the number of meals.
