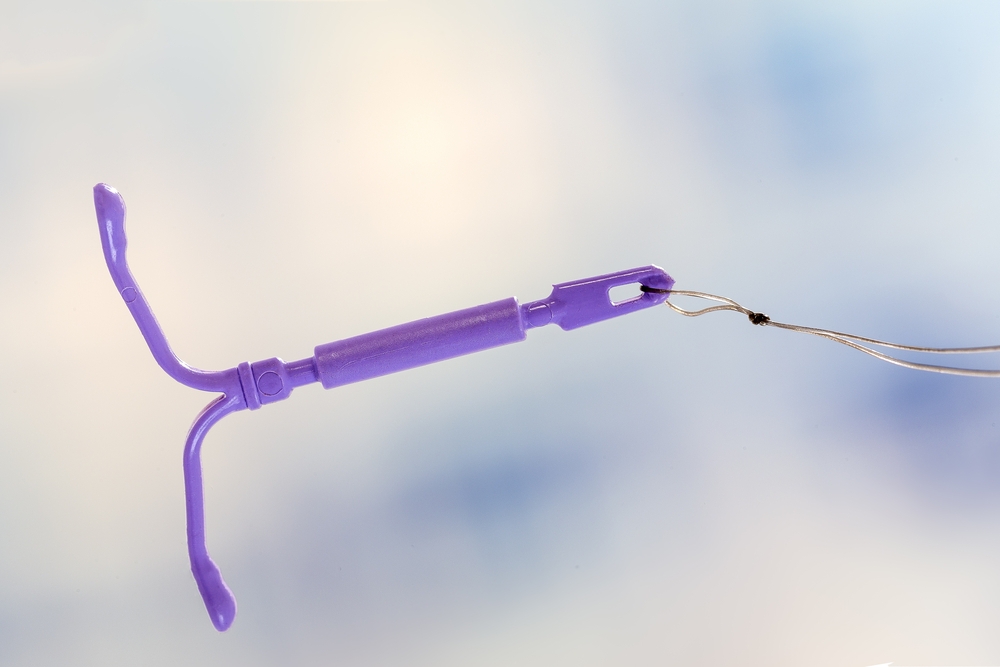
The contraceptive effect can be achieved by placing an IUD in the uterine cavity. The mechanism of action is not fully understood at present. It is mainly believed that the reaction of local tissues to foreign bodies affects the implantation of fertilized eggs, and there are the following types:
1. Toxic effects on sperm and embryos: The intrauterine device compresses the local inflammatory reaction, and the secreted inflammatory cells have toxic effects on embryos, and also produce a large number of macrophages to cover the endometrium, affecting the implantation of fertilized eggs, and can devour sperm, affecting embryo development. Copper ions of copper-containing IUD have the toxicity of separating the head and tail of sperm, making sperm lose fertilization ability.
2. Levonorgestrel IUD can inhibit ovulation in some women. Progesterone changes endometrium, which is not conducive to implantation of fertilized eggs, and changes cervical mucus characteristics at the same time, making cervix thick and not conducive to sperm penetration.
Applicable population: During the reproductive period, women who fully understand the side effects and complications of IUD and require placement can be placed after excluding contraindications.
Advantages: Contraceptive failure rate is low, which is equivalent to sterilization. It is safe, long-term, convenient, economical and reversible.
Disadvantages: There is a certain contraceptive failure rate; It has a service life and needs to be taken out or replaced when it expires. There are side effects and complications.
Type of IUD
1. Inert IUD (the first generation IUD): Made of inert materials such as metal, silica gel, plastic, etc. The commonly used metal single ring in China has been discontinued due to its high rate of falling off and pregnancy with ring.
2. Active IUD (second generation IUD): It contains active substances such as copper ions, hormones or drugs, and is divided into copper-containing IUD and drug-containing IUD.
Copper-containing IUD: It is the most widely used IUD in our country at present. It continuously releases copper ions in the body and is divided into T-shaped, V-shaped, palace-shaped and so on. Maternal music, Gini ring and love mother all belong to this kind of IUD. The contraceptive effective rate is above 90%.
Drug-containing IUD: The drug is stored in the IUD and the contraceptive effect is achieved through daily micro-release. At present, levonorgestrel-containing IUD (LNG-IUD) and indomethacin-containing IUD are mainly used in China.
How effective is contraception and whether there are side effects?
Contraceptive effect: Current research shows that research data show that the contraceptive failure rate is 0.5 ~ 0.8%, which is a safe and effective contraceptive measure.
Side effects: Irregular vaginal outflow is the most common side effect, mainly manifested as increased menstrual volume, prolonged menstrual period or a small amount of intravenous drip hemorrhage, which generally recovers gradually after 3-6 months. A few women will have leucorrhea increase or lower abdominal distending pain.
Complications:
1. IUD ectopic: improper operation, uterine perforation, or IUD is too large and hard, uterine wall is thin and soft, uterine contraction leads to IUD gradually moving out of uterine cavity. Laparoscopic or abdominal surgery is required to remove the IUD.
2. Incarceration or rupture of IUD: When placed, the uterine wall is damaged or the IUD is worn for too long, and part of the IUD body is embedded into the myometrium or ruptured. It should be taken out under ultrasound monitoring or hysteroscopy.
3. The IUD moves down or falls off: improper operation during placement, or the IUD does not conform to the size and shape of uterine cavity; Menorrhagia, cervical internal orifice is too loose. Need to replace or take out.
4. Pregnancy with IUD: Most of them are caused by ectopic, downward movement or falling off of IUD. If there is no requirement for childbirth, IUD can be taken out together during induced abortion. If there is a requirement for childbirth, pregnancy can be continued. At present, no IUD has been found to have bad effects on fertilized eggs that have been implanted.
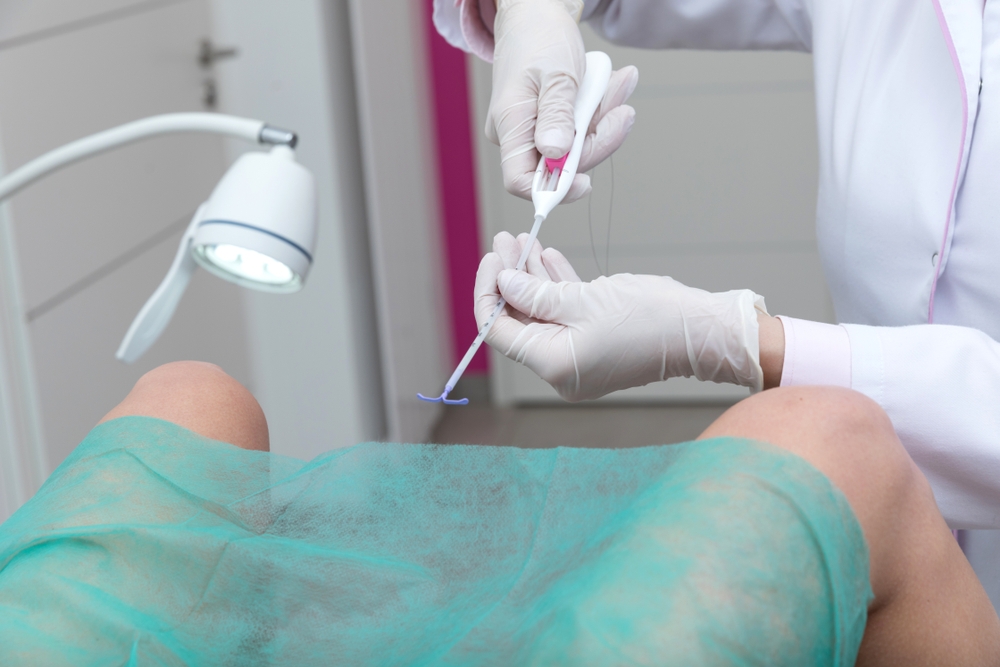
Contraindications:
1. Pregnancy or suspected pregnancy;
2. Acute inflammation of reproductive tract or active pelvic infection;
3. Induced abortion has a lot of bleeding and is suspected to be caused by pregnancy tissue residue or infection.
4. Severe deformation of uterine cavity, including: genital tract malformation, such as mediastinal uterus, double uterus, etc., or severe deformation of uterine cavity and cervical stenosis caused by uterine leiomyoma;
5. Genital tumor;
6. The cervical internal orifice is too loose, severe old cervical laceration or uterine prolapse;
7. Serious systemic diseases;
8. The uterine cavity is less than < 5.5 cm or > 9.0 cm (except for the live placement of copper-containing stent-free IUD after full-term delivery and induced labor in large months)
9. Menstrual disorder and irregular vaginal bleeding have occurred in the past 3 months;
10. Wilson’s disease or copper allergy;
11. LNG-IUD is prohibited for breast cancer patients.
What are the precautions?
1. The placement of IUD must be fully considered, voluntary and fully aware of the risks and benefits.
2. Blood routine, B-ultrasound, leucorrhea routine and other examinations shall be carried out before placement, and placement can only be carried out after there is no abnormality.
3. Follow-up is required at 1, 3, 6 and 12 months in the first year after placement, and once a year until the use is stopped.
4. In case of special circumstances, see a doctor at any time so as to find the problem in time and deal with it in time.
5. Remember the type and service life of the IUD placed, and replace or take it out in time after expiration.
Time to place IUD
1. Non-pregnant women are advised not to have sex within 3-7 days after menstruation is clean;
2. Placement immediately after induced abortion;
3. The lochia was clean 42 days after delivery, the perineal wound healed and the uterus returned to normal.
4. After spontaneous abortion and menstruation; Placement after drug abortion recovers 2 normal menstruations;
5. When menstruation is not resumed during lactation, it can be placed after pregnancy is excluded.
6. Placement within 5 days after unprotected sex can be used as one of the emergency contraceptive measures;
7. Progesterone-containing IUD is placed on the 4th to 7th day of menstruation.
Benefits other than contraception
Studies have shown that LNG-IUD can reduce menstrual blood loss, menstrual-related anemia and dysmenorrhea, treat adenomyosis and endometriosis, and reduce the risk of pelvic inflammatory disease.
