Mathematical thinking is an important thinking that determines the baby’s future learning ability.
It can not only make children learn mathematics more handy, but also determine children’s future thinking mode and intellectual development. Therefore, early mathematics enlightenment must be done well.
After reading today’s article, perhaps you have learned how to train your child’s mathematical talent in the game so that your child’s intellectual development can get twice the result with half the effort.
The first stage is to understand the concept of [number]
In fact, in addition to teaching children to count, parents can begin to teach their children to understand the correspondence between [numbers] and [numbers] when they are 1.5 years old.
For babies, one of the best learning methods is to try through sensory experience to turn abstract concepts into concrete ones.
Add leaves to a small flower
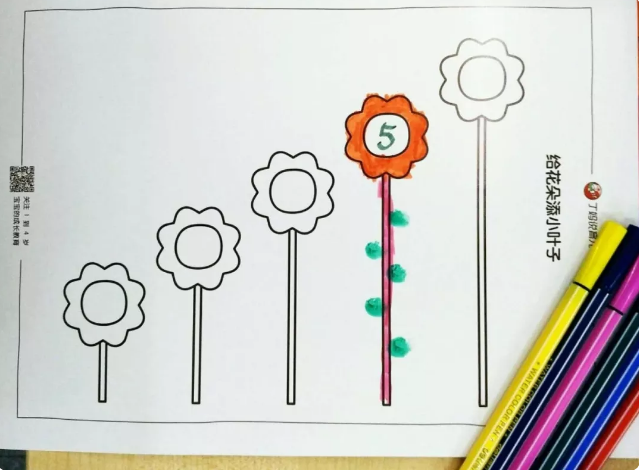

Parents will print out the digital floret template and prepare some green finger pigments.
First, let the child take crayons and paint the flowers into their favorite colors. Then you can write numbers on the flowers. Finally, dip your fingers in green pigment and you can press the corresponding number of leaves.
In the process of making flowers, the children’s fine movement ability and the ability of corresponding numbers have been trained.
Count how many
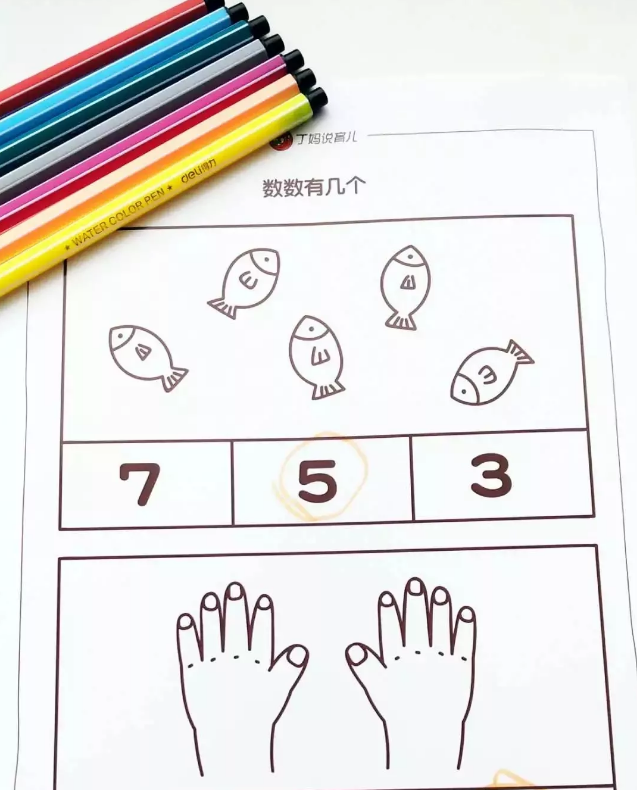

Parents first print out different numbers of cartoon patterns and digital templates;
First of all, let the children talk about it. Are the patterns full of what items? Where have we seen it?
Then you can teach your child to count. You can say, [Let’s count together. How many fish are there? One, two, three, four, five, five! So we put five circles.]
This game is suitable for children aged 1.5 ~ 2 years old. It not only enlightens the concept of number correspondence of children, but also trains children’s language expression ability.
Digital Lianliankan
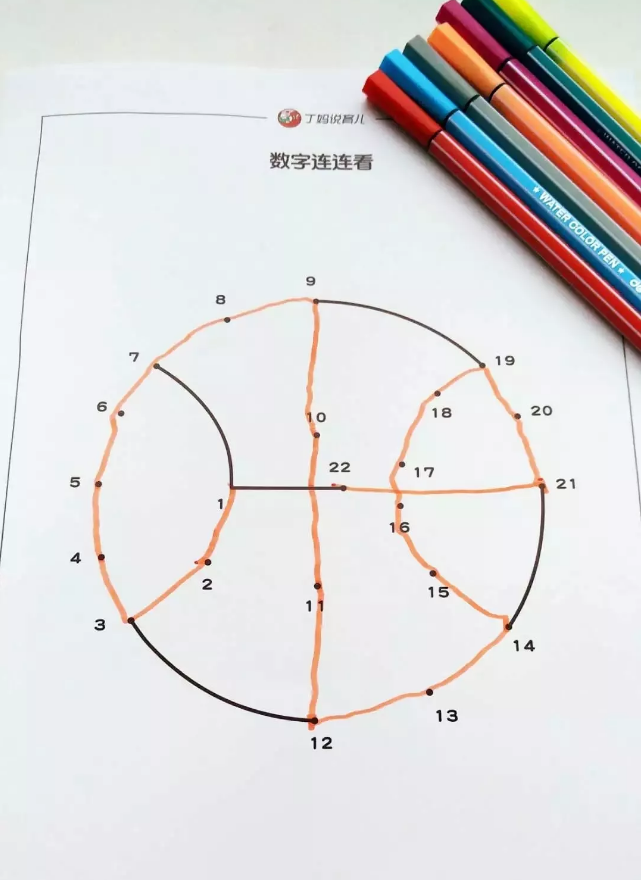
Parents print out the template first, and templates with different difficulties correspond to different digital ranges.
Then the child can count and connect the numbers in sequence.
Draw while counting, and then an interesting pattern will be revealed. Children will find it very interesting.
This game is suitable for children over 3 years old. It not only strengthens children’s counting ability, but also trains children’s hand-eye coordination ability.
The second stage is the cognition of shape.
Shape cognition is the starting point for the development of children’s spatial intelligence. Before the age of 3, the figures that children can distinguish are circles, squares, triangles and rectangles. We can carry out shape enlightenment through some games.
Shape Apple Tree
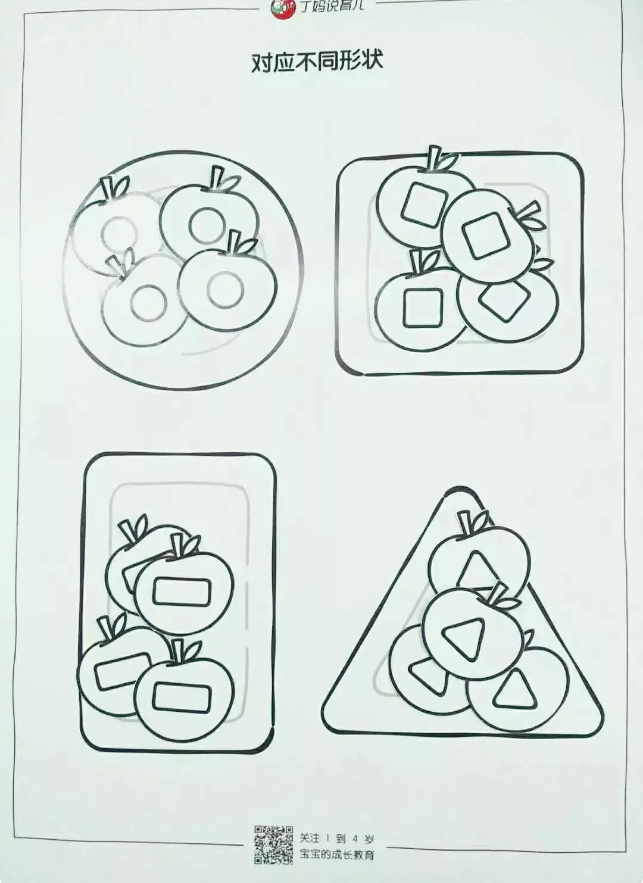
Parents first print out round, square, rectangular and triangular plates with apples of different shapes.
Teach your child to recognize these four shapes, and then let your child put apples of different shapes on plates of corresponding shapes.
This game can train children’s observation ability and shape cognition ability.
Count the edges

Parents will print out the template first so that their children can recognize the graphics and see if they all know them.
Then you can count it. The square has 4 sides. Circle the numbers 4.
When the child can identify the shapes, it means that he already knows the different characteristics of each shape, and then let the child count how many edges different shapes have, so that he can master the basic differences of different shapes.
The third stage is to learn [contrast] and measurement.
When the child is about two years old, you will find that he will take the initiative to choose a bigger cake to eat and want more candy, because the child begins to have a vague concept of [size] [how much].
At this time, we can strengthen their concept of difference in length, area and weight of things through some small games.
Compare Card
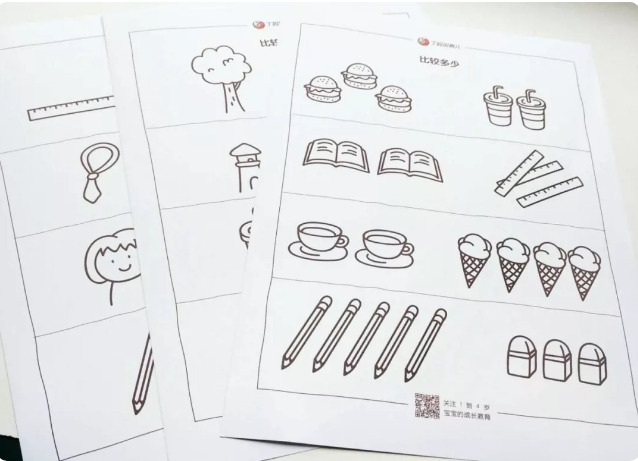
Parents will print out the cards first, with some cards that are different in length, height and weight, and then let the children point out which are more or which are longer. Don’t forget to reward the children if you answer correctly.
Measuring games
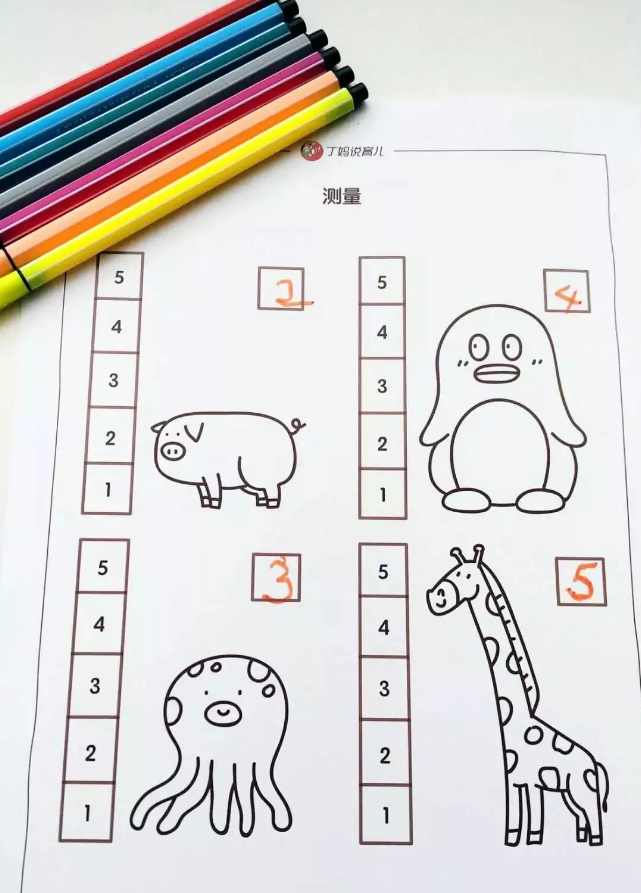

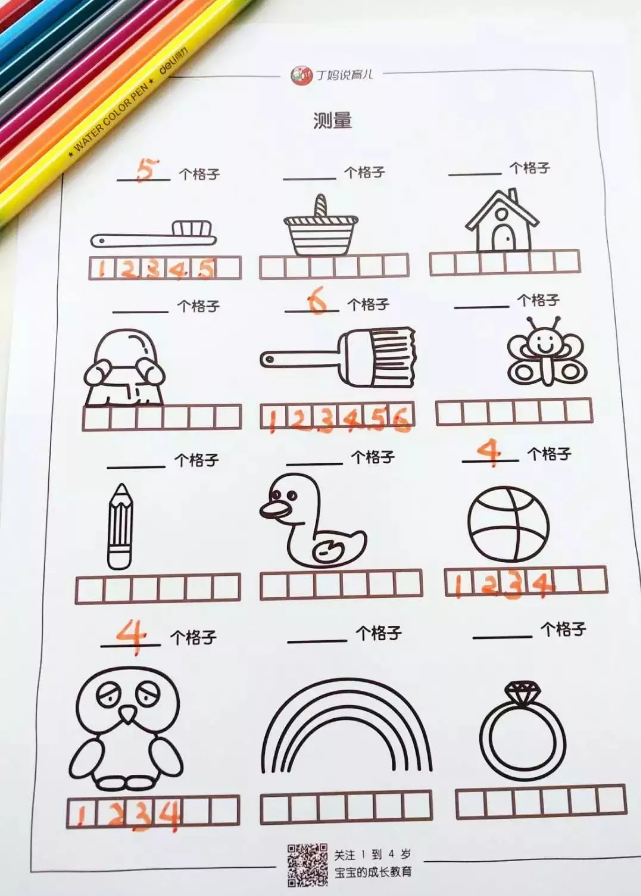
Parents first print out the card and then ask the child, what is the number corresponding to the piglet’s head? How many squares are the toothbrushes long?
Through this set of cards, children can be enlightened on the concept of [measurement].
In the [comparison card], distinguishing size, length and weight is a subjective comparison based on intuition, while this set of cards is a more accurate and objective [measurement]. From subjective to objective, this is a leap in children’s thinking.
Phase IV Contact [Number Calculation]
Most children can master addition and subtraction within 5 when they are 3 ~ 4 years old. 4 ~ 5 years old can master within 10; 5 ~ 6 years old, can master addition and subtraction within 20 ~ 25 years old.
Therefore, mathematical calculations can be enlightened in small home games.
Addition Operation of Colored Ball
Children are young and do not have abstract thinking, so when teaching children addition and subtraction at the beginning, they need to make full use of physical objects.
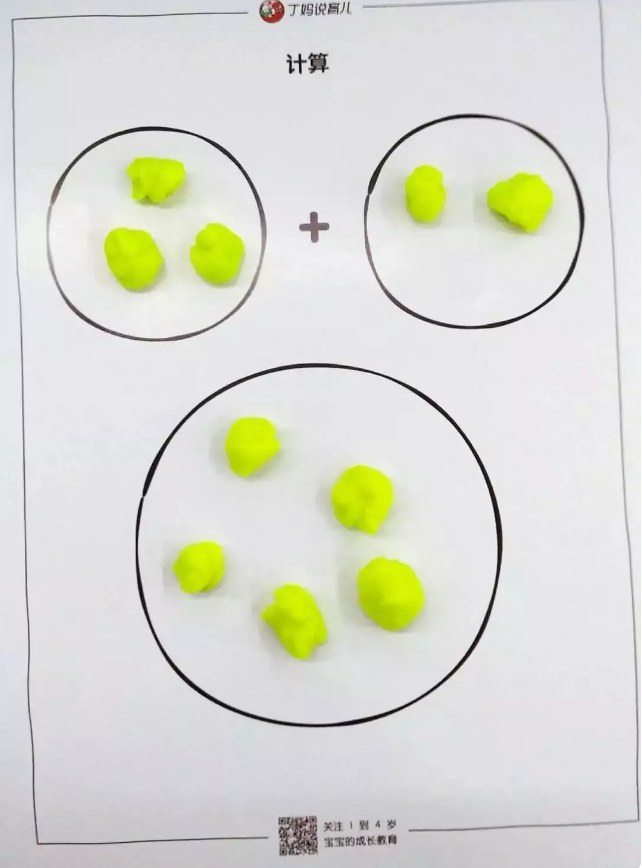

For example, using the above template and combining the ultra-light clay or plasticine in the home to make small colored balls can be used as a good enlightenment tool for addition operations.
Let the children throw dice at random. If they throw 3 and 2, put 3 small colored balls in one box, 2 on the other side, and count them together. How much is the total?
Add Quantity to Draw
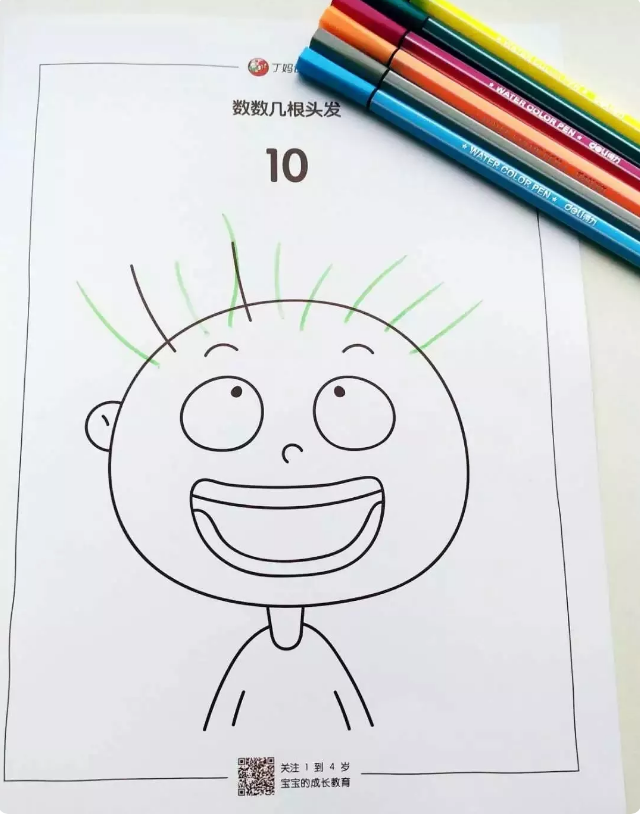

Parents print out the card first and count the hair of the children on the card together.
Then let the child add hair to the card. In the process, the child understands that 2 hairs plus 8 hairs become 10 hairs.
This game is also for children to do initial addition enlightenment, turning abstract addition into image patterns.
Mathematics is a very important basic subject. Parents must not miss the best period of their children’s mathematics enlightenment.
However, it should be noted that parents should not act too hastily when playing math enlightenment games with their children, and should arrange them according to their children’s interests.
If the child does not like a certain game, then try another one. Protecting the child’s interest in mathematics is more important than the speed of absorption.
